Why use conductive polymers?
With appropriate design & utilisation, conductive plastics can replace metals in many thermal management applications
There is a growing demand for thermal management of components, devices and systems in established and emerging areas such as electronics, LED lighting and battery technology/e-powertrain.
Metals are traditionally utilised here for applications such as heat sinks, housings and covers, but there are drawbacks and limitations to their use and alternative materials offering new design advantages are increasingly sought after. Thermally conductive polymers are a potential candidate which, if designed and utilised correctly, can operate successfully in this arena.
1. Performance
Tailoring of thermal conductivity properties leads to enhanced performance from application specific materials.
2. Environment
Weight reduction leading to enhanced fuel consumption.
3. Longevity
Inherent corrosion resistance, enhancing product quality and lifetime.
4. Economy
Part consolidation opportunities leading to a reduction in number of components and costs.
5. Design
Capability to injection mould/overmould enabling design freedom and easier processing for more complex shapes.
6. Scope
Potential to offer electrically insulating or conductive solutions, expanding the scope of possible applications.
In-house
Netzsch thermal conductivity analysis
Mauris cursus mattis molestie a iaculis. Viverra ipsum nunc aliquet bibendum enim facilisis gravida. Faucibus vitae aliquet nec ullamcorper sit amet risus.
Benefits of KONDUCT®
Amet nulla facilisi morbi tempus iaculis. Euismod nisi porta lorem mollis aliquam ut porttitor. Enim sit amet venenatis urna cursus eget nunc scelerisque.
Turpis massa tincidunt dui ut ornare lectus sit amet. Mauris cursus mattis molestie a iaculis. Viverra ipsum nunc aliquet bibendum enim facilisis gravida. Faucibus vitae aliquet nec ullamcorper sit amet risus. Lectus nulla at volutpat diam ut.
1. Flexibility
With the on-site capabilities and facilities, Radical Materials are able to support small to large custom developments from lab scale all the way up to full production.
2. Testing & Reporting
A wide suite of test facilities are available to support developments. These include mechanical tests as well as properties such as thermal conductivity and surface resistivity.
3. R&D focus
A continuing focus on new and novel technologies to bring advantages and progression to conductive polymers.
Electrical conductivity
explained
Polymers are typically classed as electronically insulating materials and are often used for insulation applications in electrical devices. However, there are many applications which call for traditional benefits of polymers over, for example, metals (low weight, no corrosion etc) whilst also requiring specific levels of electrical conductivity and/or shielding performance.
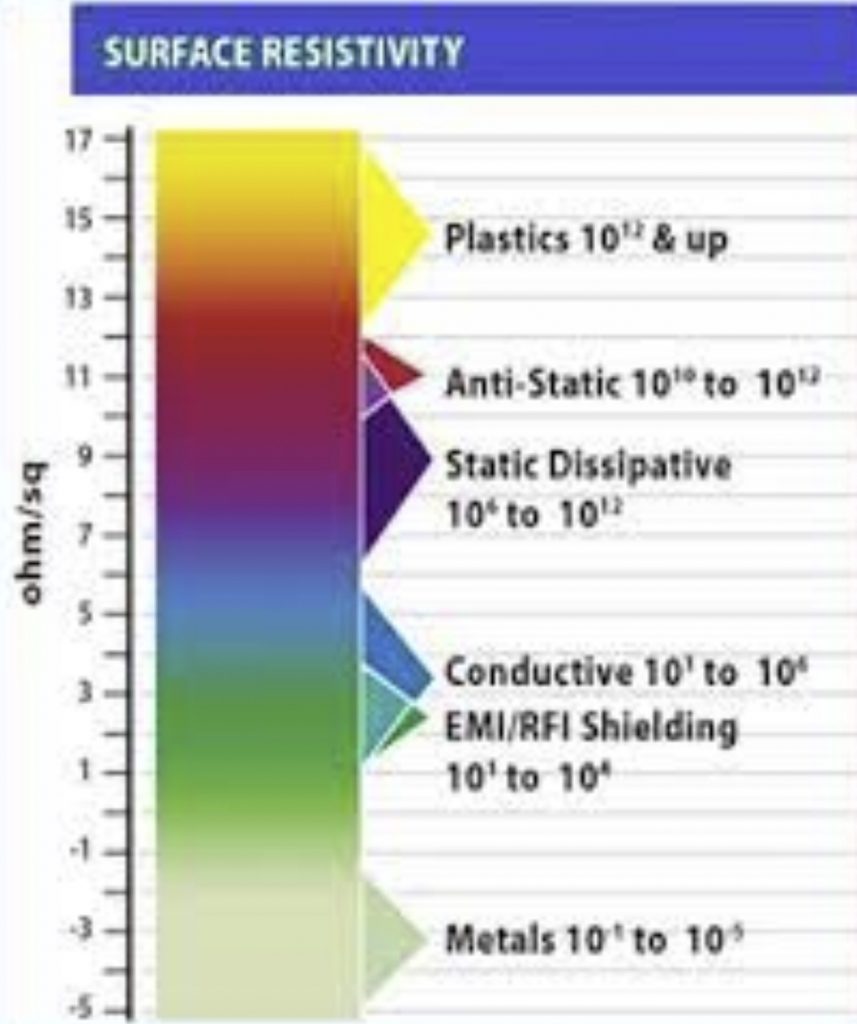
The below chart illustrates the range of surface resistivity required and possible between unfilled plastics, modified plastics and metals:
Thermal conductivity
explained
Heat transfer occurs via three main mechanisms. When designing for thermal management and the control thereof, all of these mechanisms need to be considered as a whole, along with their effect on the entire system.
• Radiation
Energy transfer away from an emitting source via electromagnetic waves. Can occur through a vacuum or solid/fluid.
• Convection
Energy transfer between a solid surface and a surrounding fluid (liquid/air). Such transfer is related to the conditions of the whole system in consideration and not to a specific material property.
• Conduction
Transfers heat via molecular collisions and requires physical contact. The process itself depends upon the existing temperature gradient, cross-section/dimensions of the component and the physical properties of the material in question (thermal conductivity).
EMI/RFI Shielding
explained
Electromagnetic shielding is the practice of reducing the electromagnetic field in a space by blocking the field with barriers of conductive or magnetic materials. Such shielding is necessary to prevent mutual interference of devices causing disturbance or breakdown of operation, as well as protecting humans from associated health risks. EMI shielding (radio/microwaves) of both electronics and potentially the radiation source is becoming increasingly important to the high demands of today’s society.
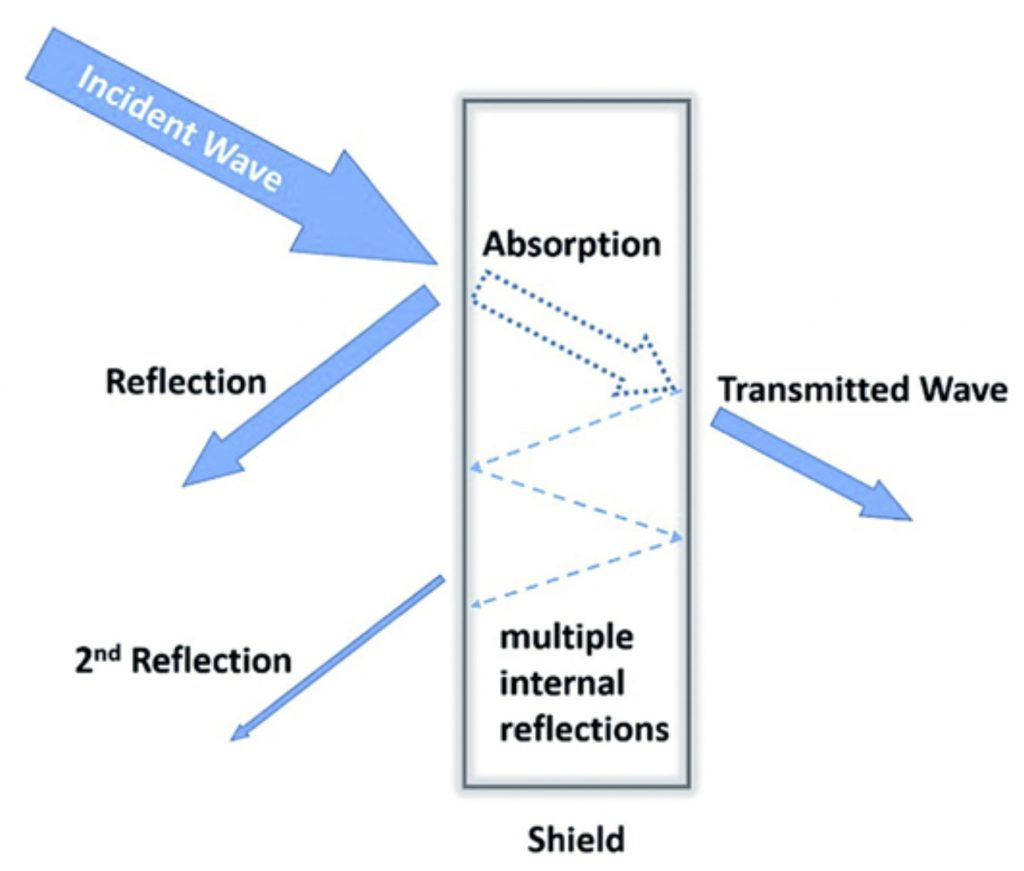
When EM waves impinge on an object’s surface, they undergo one of three main mechanisms – reflection, absorption or transmission. In order to arrest the EM wave, it should be reflected or absorbed by the shielding material.
Solid metal components (Cu, Al, Ag, Ni) have traditionally been utilised successfully, but suffer from the drawbacks of high weight, susceptibility to corrosion and uneconomical processing. More interest now focuses on composite systems of typically an insulating polymer matrix with specific fillers. These fillers can include magnetic materials as well as electrical conductivity enhancers such as carbon nanotubes, graphene and structured carbon blacks.
Bespoke product developments
Masterbatch and compound can be developed to suit specific requirements and applications.
Turpis massa tincidunt dui ut ornare lectus sit amet. Mauris cursus mattis molestie a iaculis. Viverra ipsum nunc aliquet bibendum enim facilisis gravida. Faucibus vitae aliquet nec ullamcorper sit amet risus. Lectus nulla at volutpat diam ut.
1. Research & development
With the on-site capabilities and facilities, Radical Materials are able to support small to large custom developments from lab scale all the way up to full production.
2. Testing capabilities
A wide suite of test facilities are available to support developments. These include mechanical tests as well as properties such as thermal conductivity and surface resistivity.
3. Certification
A wide suite of test facilities are available to support developments. These include mechanical tests as well as properties such as thermal conductivity and surface resistivity.
4. Manufacturing
A continuing focus on new and novel technologies to bring advantages and progression to conductive polymers.





